LanceDB will automatically vectorize the data both at ingestion and query time. All you need to do is specify which model to use.
We support most popular embedding models like OpenAI, Hugging Face, Sentence Transformers, CLIP, and more.
First, import the necessary LanceDB components:
import lancedb
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registrylancedb: The main database connection and operationsLanceModel: Pydantic model for defining table schemasVector: Field type for storing vector embeddingsget_registry(): Access to the embedding function registry. It has all the supported as well custom embedding functions registered by the userEstablish a connection to your LanceDB instance:
db = lancedb.connect(...)Choose and configure your embedding model:
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", )This creates a Sentence Transformers embedding function using the BGE model. You can:
"sentence-transformers" to other providers like "openai", "cohere", etc.device="cuda" for GPU acceleration if availableCreate a Pydantic model that defines your table structure:
class Words(LanceModel):
text: str = model.SourceField()
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField() SourceField(): This field will be embeddedVectorField(): This stores the embeddingsmodel.ndims(): Sets vector dimensions for your modelGo back to LanceDB Cloud and check that the table and schema were created:
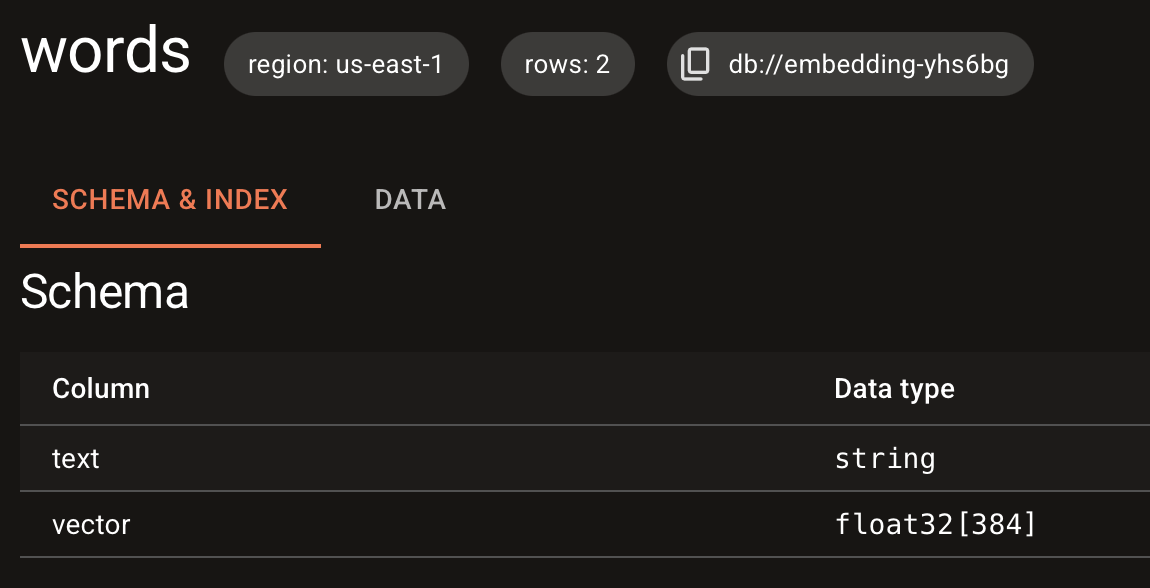
Create a table with your schema and add data:
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words)
table.add([
{"text": "hello world"},
{"text": "goodbye world"}
])The table.add() call automatically:
Note: On LanceDB cloud, automatic query embedding is not supported. You need to pass the embedding vector directly.
Search your data using natural language queries:
query = "greetings"
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
print(actual.text)The search process:
LanceDB currently supports the Embedding API via SDKs in Python, Typescript and Rust .
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registryimport * as lancedb from "@lancedb/lancedb";
import "@lancedb/lancedb/embedding/openai";
import { LanceSchema, getRegistry, register } from "@lancedb/lancedb/embedding";
import { EmbeddingFunction } from "@lancedb/lancedb/embedding";
import { type Float, Float32, Utf8 } from "apache-arrow";use std::{iter::once, sync::Arc};
use arrow_array::{Float64Array, Int32Array, RecordBatch, RecordBatchIterator, StringArray};
use arrow_schema::{DataType, Field, Schema};
use futures::StreamExt;
use lancedb::{
arrow::IntoArrow,
connect,
embeddings::{openai::OpenAIEmbeddingFunction, EmbeddingDefinition, EmbeddingFunction},
query::{ExecutableQuery, QueryBase},
Result,
};Here are some examples of queries in multiple languages.
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
func = get_registry().get("openai").create(name="text-embedding-ada-002")
class Words(LanceModel):
text: str = func.SourceField()
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words, mode="overwrite")
table.add([{"text": "hello world"}, {"text": "goodbye world"}])
query = "greetings"
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
print(actual.text) const db = await lancedb.connect(databaseDir);
const func = getRegistry()
.get("openai")
?.create({ model: "text-embedding-ada-002" }) as EmbeddingFunction;
const wordsSchema = LanceSchema({
text: func.sourceField(new Utf8()),
vector: func.vectorField(),
});
const tbl = await db.createEmptyTable("words", wordsSchema, {
mode: "overwrite",
});
await tbl.add([{ text: "hello world" }, { text: "goodbye world" }]);
const query = "greetings";
const actual = (await tbl.search(query).limit(1).toArray())[0];#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let tempdir = tempfile::tempdir().unwrap();
let tempdir = tempdir.path().to_str().unwrap();
let api_key = std::env::var("OPENAI_API_KEY").expect("OPENAI_API_KEY is not set");
let embedding = Arc::new(OpenAIEmbeddingFunction::new_with_model(
api_key,
"text-embedding-3-large",
)?);
let db = connect(tempdir).execute().await?;
db.embedding_registry()
.register("openai", embedding.clone())?;
let table = db
.create_table("vectors", make_data())
.add_embedding(EmbeddingDefinition::new(
"text",
"openai",
Some("embeddings"),
))?
.execute()
.await?;
let query = Arc::new(StringArray::from_iter_values(once("something warm")));
let query_vector = embedding.compute_query_embeddings(query)?;
let mut results = table
.vector_search(query_vector)?
.limit(1)
.execute()
.await?;
let rb = results.next().await.unwrap()?;
let out = rb
.column_by_name("text")
.unwrap()
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<StringArray>()
.unwrap();
let text = out.iter().next().unwrap().unwrap();
println!("Closest match: {}", text);
Ok(())
}Learn about using the existing integrations and creating custom embedding functions in the Embedding Guide .\
Check out some Basic Usage tips . After that, we’ll teach you how to build a small app.